Overview of Network Installation and Configuration
Network installation and configuration form the backbone of modern connectivity, encompassing everything from selecting and installing network hardware to wiring an office network and ensuring seamless operation. At its core, network installation involves the physical and logical setup of infrastructure that allows devices to communicate, share resources, and access the internet. This includes tasks like install network cabling, network equipment installation, and configuring network settings to optimize performance. What is network configuration? It describes how a network is arranged, including the arrangement of devices, protocols, and security measures that govern data flow.
In essence, network design and installation go hand-in-hand, starting with planning the layout – such as a star topology for efficient cable configuration—and progressing to the actual deployment. For instance, in a commercial network installation, this might involve integrating enterprise network setup with advanced features like VLANs for segmentation. Home networking installation, on the other hand, focuses on simpler wired home network installation, often using Cat6 B config for reliable Ethernet connections. Professional home network installation services can elevate this by incorporating network cable management software to monitor and maintain the system.
The process also extends to network infrastructure installation, where components like routers, switches, and servers are integrated. Computer network server setup is crucial here, as it enables centralized data storage and management. Types of network configuration vary, from basic LAN setups in homes to complex WANs in organizations. A network of computers inside an organization, often called an intranet, relies on robust infrastructure installation to function effectively. The current standard for wired ethernet networks is Cat 6 or higher, ensuring high-speed data transfer.
Computers need this hardware to connect to a network: network interface cards (NICs), switches for local traffic, and routers for internet routing. Without proper netzwerk installation (a term often used in German-speaking regions for network setup), systems can face inefficiencies. Similarly, netværk installation in Nordic contexts emphasizes reliable cabling to withstand environmental factors. Overall, network install processes must address potential challenges like network installation and troubleshooting from the outset to avoid disruptions.
Importance of Proper Network Setup in Modern Environments
In today’s digital landscape, the importance of proper network setup cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts productivity, security, and scalability across various environments. With the explosion of remote work and digital transformation, a well-executed office network installation ensures uninterrupted access to resources, reducing the risk of downtime that can cripple operations. For example, improper configuring network can lead to vulnerabilities, exposing businesses to cyber threats—statistics from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) indicate that misconfigurations account for a significant portion of data breaches.
Globally, the reliance on networks is evident in the sheer volume of connected devices. According to Statista, the total number of Internet of Things (IoT) connected devices worldwide is projected to reach approximately 19.8 billion by 2025, with total connected devices (including non-IoT) exceeding 30 billion. This surge underscores the need for robust network configuration basics, as poorly arranged networks struggle to handle the data load. Wikipedia’s entry on the Internet of Things highlights how these devices form interconnected ecosystems, maintained by networks that form the internet through ISPs and backbone providers.
Downtime statistics further emphasize this: Gartner reports that the average cost of network downtime for businesses is around $5,600 per minute, leading to potential losses of hundreds of thousands per hour in critical sectors. For enterprises, this can translate to millions annually; a Ponemon Institute study cited by Atlassian estimates costs ranging from $100,000 to over $540,000 per hour depending on the industry. Proper IT network installation minimizes these risks by incorporating redundancy and automated troubleshooting.
In home settings, the importance lies in seamless connectivity for streaming, gaming, and smart devices. Home network installers often stress that inadequate network set up can result in frequent dropouts, affecting quality of life. Official data from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) shows that over 80% of U.S. households rely on home networks, with improper setups contributing to 30% of support calls. Networking installations that prioritize security, like firewall configurations, protect against unauthorized access, which is vital as cyber attacks on home networks have risen by 15% year-over-year per government reports.
| Statistic | Value | Source |
| Global IoT Devices by 2025 | 19.8 billion | Statista (2025) |
| Total Connected Devices by 2025 | Over 30 billion | Statista (2025) |
| Average Downtime Cost per Minute | $5,600 | Gartner (via Pingdom) |
| High-End Downtime Cost per Hour | Up to $540,000 | Atlassian/Ponemon |
| Cyber Attacks on Home Networks Increase | 15% YoY | FCC Reports |
Scope of This Guide: Covering Home, Office, Commercial, and Enterprise Networks
This comprehensive guide delves into every facet of network installation and upgrades, providing step-by-step configuration of network processes tailored to diverse needs. From home networking wired setups, complete with wired home network diagram examples, to sophisticated enterprise network setup, we cover the spectrum. Office network installation is a key focus, addressing wiring an office network and network drop installation for multi-device environments.
For commercial network installation, the guide explores scalable solutions like infrastructure network install for retail or healthcare facilities, incorporating computer networking installation best practices. Enterprise-level topics include a network of computers inside an organization, with emphasis on security and performance. We also touch on international variations, such as netzwerkinstallation in German-regulated markets, ensuring compliance with local standards.
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast tackling home network installation or a professional handling commercial network, this resource includes troubleshoot network wiring tips, connection guide for cabling, and network installation and troubleshooting strategies. It addresses questions like “is it safe to cut live data cabling?” (spoiler: no, always power down first) and integrates network cable management for long-term efficiency. The scope extends to advanced topics like install software across computers on a large network, making it a one-stop reference.
Key Benefits and Potential Cost Savings
Investing in proper network installation yields numerous benefits, including enhanced reliability, faster speeds, and improved security. A well-configured system reduces energy consumption by up to 20%, per U.S. Department of Energy data, through efficient hardware utilization. Benefits also include scalability for future upgrades, minimizing the need for frequent overhauls.
Cost savings are substantial when comparing DIY vs. professional approaches. For a small office network installation (5-15 drops), DIY costs range from $500 to $2,000 in materials and tools, covering basics like Cat6 cabling and switches. Professional services, however, average $2,500 to $7,500, including labor and warranties, offering peace of mind for complex setups. This can result in savings of $1,000-$5,000 for those skilled in network install, but professionals often prevent costly errors, recouping investment through avoided downtime.
In larger commercial network installation, enterprises save 15-25% on operational costs with optimized configurations, as per Wikipedia’s networking economics references. Network server setup alone can cut data management expenses by centralizing resources.
| Approach | Average Cost (Small Office) | Benefits | Potential Savings |
| DIY | $500-$2,000 | Hands-on control, lower upfront | Up to $5,000 vs. pro |
| Professional | $2,500-$7,500 | Expertise, warranties | Long-term via reduced downtime ($100K+ avoided) |
| Hybrid (DIY with Consultation) | $1,500-$4,000 | Balanced cost-efficiency | 10-20% on maintenance |
Understanding Network Basics
What is Network Configuration?
Network configuration describes how a network is arranged, encompassing the setup of hardware, software, and protocols that enable devices to communicate effectively. It involves configuring network settings to ensure seamless data transfer, security, and scalability. This process includes defining IP addresses, setting up routers and switches, and establishing security measures like firewalls. Network configuration step-by-step involves tasks such as assigning static or dynamic IPs, configuring VLANs for segmentation, and optimizing bandwidth allocation.
Proper network configuration is critical for network installation and troubleshooting, as it minimizes connectivity issues and enhances performance. For example, in an office network installation, configuration ensures that all devices—computers, printers, and servers—communicate efficiently. Misconfigurations, such as incorrect subnet masks, are responsible for approximately 20% of network outages, according to a 2023 study by Cisco. Whether it’s a home network installation or a commercial network, understanding how a network is arranged is the foundation for reliable connectivity.
Types of Network Configuration
Networks come in various configurations, each tailored to specific needs, environments, and scales. The primary types include:
- Local Area Network (LAN): Connects devices within a limited area, like a home or office. Ideal for wiring an office network or home networking wired setups.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Spans large geographic areas, connecting multiple LANs, often used in enterprise network setup or by ISPs.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): Uses Wi-Fi for connectivity, common in home networking installation and commercial network installation for flexibility.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Covers a city or campus, bridging multiple LANs, often seen in large commercial network setups.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Secures remote connections over the internet, critical for a network of computers inside an organization.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): Connects personal devices, like smartphones and laptops, typically in home network installers’ projects.
Each type serves distinct purposes. For instance, LANs dominate office network installation due to their speed and reliability, while WANs are essential for global enterprises. According to Statista, LANs account for 60% of enterprise network configurations globally, with WLANs growing by 15% annually due to mobility demands.
Network Configuration Basics
Network configuration basics involve setting up the foundational elements to ensure a network operates efficiently. This includes:
- IP Addressing: Assigning unique identifiers to devices, either statically or via DHCP for dynamic allocation.
- Subnetting: Dividing networks into smaller segments to improve performance and security, crucial in IT network installation.
- Routing: Configuring routers to direct data traffic, a key step in configuring network for offices or homes.
- Security Settings: Implementing firewalls and encryption, especially in professional home network installation to protect against threats.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizing traffic to ensure critical applications, like VoIP, perform optimally in commercial network installation.
These steps are universal across network install types, from netzwerk installation in German-regulated environments to netværk installation in Nordic regions. A 2024 report by the IEEE indicates that proper configuration reduces latency by up to 30% in high-traffic networks. For beginners, understanding these basics is essential before tackling tasks like install software across computers on a large network.
Networks That Form the Internet Are Maintained By
The internet is a vast network of networks, maintained by Internet Service Providers (ISPs), Tier 1 backbone providers, and regional network operators. These entities manage the infrastructure network install that connects continents through undersea cables, satellite links, and high-capacity fiber optics. ISPs handle last-mile connectivity, delivering internet to homes and businesses, while backbone providers like Level 3 and Cogent maintain high-speed global connections.
Wikipedia’s entry on the Internet highlights that Tier 1 providers, such as AT&T and Verizon, operate the core infrastructure, handling approximately 50% of global internet traffic. Regional ISPs, crucial for home networking installation, rely on these backbones to provide access. Network server setup at data centers ensures redundancy and uptime, with global internet uptime averaging 99.99%, per Cloudflare’s 2024 metrics. This infrastructure supports everything from home network installers to enterprise-level network installation.
The Current Standard for Wired Ethernet Networks
The current standard for wired Ethernet networks is Category 6 (Cat6) and Category 6a (Cat6a) cabling, offering speeds up to 10 Gbps over distances of 55-100 meters. Cat6 is widely used in office network installation and wired home network installation due to its balance of cost and performance. Cat6a, with enhanced shielding, supports longer runs and is ideal for commercial network installation or enterprise network setup where future-proofing is key. Cat7 and Cat8 are emerging for ultra-high-speed applications, but adoption is limited due to cost, with Cat6 covering 85% of installations, per a 2023 TIA report.
These standards support robust network drop installation and computer network wiring. For instance, Cat6 B config is preferred for its noise resistance, critical in high-density environments. The connection guide for Cat6 includes proper termination to avoid signal loss, which can reduce performance by 10-15% if mishandled.
Computers Need This Hardware to Connect to a Network
To connect to a network, computers require specific hardware components:
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Enables wired or wireless connectivity, embedded in most modern devices.
- Switches: Manage local traffic in LANs, essential for wiring an office network or home networking wired setups.
- Routers: Direct traffic between networks, critical for internet access in network set up.
- Access Points: Extend WLAN coverage, common in commercial network installation.
- Cabling: Cat6 or higher for reliable computer network wiring.
Network equipment installation ensures these components work cohesively. For example, a gigabit switch can handle 1000 Mbps, supporting high-speed LANs. A 2024 IDC study notes that 70% of network performance issues stem from outdated hardware, making upgrades vital. Network cable management ensures organized wiring, reducing troubleshooting time by 25%.
Comparison of Network Types
| Network Type | Use Case | Speed (Typical) | Cost (Approx.) | Common Applications |
| Home (LAN/WLAN) | Home networking installation | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps | $100-$1,000 | Streaming, gaming, smart devices |
| Office (LAN) | Office network installation | 1-10 Gbps | $1,000-$10,000 | File sharing, VoIP, intranet |
| Commercial (LAN/WAN) | Commercial network installation | 1-40 Gbps | $5,000-$50,000 | Retail, healthcare, multi-site |
| Enterprise (WAN/MAN) | Enterprise network setup | 10-100 Gbps | $50,000-$500,000 | Data centers, global operations |
This table compares key network types, reflecting data from industry reports like Gartner’s 2024 networking analysis. Home networks prioritize affordability, while enterprise setups demand scalability, with costs scaling accordingly. Networking installations vary in complexity, with troubleshoot network wiring being a common challenge across all types.
Planning Your Network Design and Installation
Network Design and Installation Fundamentals
Network design and installation form the critical first step in creating a reliable and efficient network, whether for home networking installation, office network installation, or commercial network installation. This process involves defining the network’s purpose, scale, and performance requirements to ensure seamless connectivity. Network design encompasses selecting the right topology, hardware, and cabling, while installation translates this plan into a functional system through network equipment installation and install network cabling.
Key fundamentals include scalability, redundancy, and security. For instance, a well-planned network set up minimizes bottlenecks and supports future network installation and upgrades. In enterprise network setup, design considerations include high-availability configurations to prevent downtime. According to a 2024 CompTIA report, 65% of IT professionals cite poor planning as a leading cause of network inefficiencies, emphasizing the need for thorough preparation. Proper network design and installation also streamline network installation and troubleshooting by reducing errors during deployment.
Assessing Needs: Home Networking Installation vs. Office Network Installation vs. Commercial Network Installation
Assessing needs is pivotal to tailoring a network to its intended use. Each environment—home, office, or commercial—has unique requirements:
- Home Networking Installation: Focuses on simplicity and cost-effectiveness, supporting streaming, gaming, and smart devices. Typical setups involve a single router, a switch, and Cat6 B config for wired home network installation. Speed requirements range from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps.
- Office Network Installation: Prioritizes reliability and scalability for multiple users, printers, and servers. Wiring an office network often involves network drop installation for 10-50 devices, requiring robust switches and VLAN configurations. Speeds typically range from 1-10 Gbps.
- Commercial Network Installation: Demands high performance and uptime for retail, healthcare, or multi-site operations. These networks often integrate wired and wireless solutions, with enterprise-grade routers and fiber optics for backbone connectivity. Speeds can reach 40 Gbps or higher.
A 2023 Gartner study notes that 70% of businesses misjudge their network capacity needs, leading to over- or under-provisioning. Assessing needs involves analyzing user count, device types, and data traffic. For example, a small office may need 10-20 network drops, while a commercial network might require 100+ drops for a multi-floor building.
Site Survey and Layout Planning
A site survey is essential for effective network infrastructure installation, identifying physical and environmental factors that impact performance. This involves mapping the area, noting obstacles like walls or interference sources, and planning cable routes. For wired home network installation, a wired home network diagram might show a central router connected to devices via Cat6 cables in a star topology. In office or commercial settings, surveys account for multiple floors, server rooms, and high-traffic areas.
Key steps include:
- Measuring distances for cable runs (Cat6 supports up to 100 meters for 1 Gbps).
- Identifying power sources for network equipment installation.
- Planning network drop installation points for optimal coverage.
- Ensuring cable configuration avoids electromagnetic interference.
Diagrams are critical for visualizing layouts. For example, a home network diagram might depict a router in the living room, with Cat6 cables running to bedrooms and a media center. A 2024 TIA standard emphasizes that proper site surveys reduce cabling errors by 30%. Tools like Ekahau or NetSpot assist in professional home network installation and commercial setups, ensuring precise planning.
Budgeting for Network Infrastructure Installation
Budgeting for network infrastructure installation requires balancing upfront costs with long-term performance. Costs vary by scale:
- Home Networking Installation: $100-$1,000 for hardware (router, switch, Cat6 cables) and $0-$500 for labor if using home network installers.
- Small Office (5-15 drops): $500-$5,000, including $200-$1,000 for cabling, $300-$2,000 for hardware, and $0-$2,000 for labor.
- Commercial Network Installation: $5,000-$50,000, with $2,000-$10,000 for cabling, $3,000-$20,000 for enterprise-grade hardware, and $0-$20,000 for professional services.
| Network Type | Hardware Cost | Cabling Cost | Labor Cost | Total (Approx.) |
| Home | $50-$500 | $50-$500 | $0-$500 | $100-$1,500 |
| Small Office | $300-$2,000 | $200-$1,000 | $0-$2,000 | $500-$5,000 |
| Commercial | $3,000-$20,000 | $2,000-$10,000 | $0-$20,000 | $5,000-$50,000 |
These estimates align with industry data from Cabling Installation & Maintenance (2024), noting that labor costs drop significantly for DIY setups but risk errors. Budgeting should also account for network cable management software ($100-$1,000 annually) to streamline maintenance.
Selecting Network Topology
Network topology defines how devices are interconnected, impacting performance and scalability. Common topologies include:
- Star Topology: Centralized through a switch or router, ideal for home networking wired and office network installation due to ease of troubleshooting.
- Mesh Topology: Devices connect directly, enhancing redundancy for commercial network installation but increasing cabling costs.
- Bus Topology: Older, less common, used in legacy systems but prone to failures.
- Ring Topology: Devices form a loop, used in specific enterprise network setup scenarios for predictable data flow.
Star topology dominates, with 80% of modern LANs adopting it, per a 2023 IEEE report, due to its simplicity and scalability. For example, in wiring an office network, a star topology ensures each network drop connects to a central switch, simplifying network installation and troubleshooting. Mesh is gaining traction in enterprise setups, with 15% adoption for high-availability needs.
Legal and Safety Considerations
Legal and safety considerations are critical in network install processes. Regulations vary by region; for instance, netzwerkinstallation in Germany must comply with VDE standards, while netværk installation in Nordic countries adheres to EU electrical codes. Key considerations include:
- Permits: Required for commercial network installation in multi-tenant buildings, costing $100-$1,000 depending on location.
- Safety Protocols: Is it safe to cut live data cabling? No—cutting live cables risks electrical shock and data loss. Always power down and use insulated tools.
- Fire Codes: Cabling must use plenum-rated materials in air-handling spaces, per NFPA 70 standards, adding 10-20% to costs.
- Data Privacy: Configuring network security to comply with GDPR or CCPA for enterprise setups.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) reports that 5% of workplace electrical incidents involve improper cabling practices. Proper training reduces risks, especially in computer network wiring.
Statistics on Network Failures Due to Poor Planning
Poor planning is a leading cause of network failures, with significant operational impacts. A 2024 Cisco study found that 40% of network downtime results from misconfiguration or inadequate planning, leading to an average of 4 hours of downtime per incident. Additionally, Gartner estimates that businesses lose $100,000-$540,000 per hour of downtime, depending on the industry.
| Failure Cause | Percentage of Downtime | Average Cost per Hour | Source |
| Misconfiguration | 40% | $100,000-$540,000 | Cisco (2024) |
| Hardware Failure | 25% | $50,000-$200,000 | Gartner (2023) |
| Cabling Issues | 20% | $20,000-$100,000 | TIA (2024) |
These statistics highlight the importance of thorough planning, from site surveys to selecting the right topology, to avoid costly disruptions in IT network installation.
Selecting and Installing Network Hardware
Select and Install Network Hardware Overview
Selecting and installing network hardware is a cornerstone of effective network installation, whether for home networking installation, office network installation, or commercial network installation. This process involves choosing the right components—such as routers, switches, and servers—that align with the network’s scale, performance needs, and budget. Network equipment installation requires careful planning to ensure compatibility, scalability, and reliability. Proper selection of hardware supports configuring network settings efficiently, reducing the need for frequent network installation and upgrades.
The process begins with assessing the network’s requirements, such as bandwidth, user count, and security demands. For example, a wired home network installation might prioritize cost-effective routers, while an enterprise network setup demands high-performance switches for heavy data traffic. According to a 2024 IDC report, 70% of network performance issues stem from outdated or mismatched hardware, highlighting the importance of informed selection. Installing hardware correctly, following a connection guide, ensures seamless integration and minimizes network installation and troubleshooting efforts.
Key Components: Routers, Switches, Access Points
The backbone of any network lies in its core components: routers, switches, and access points. Each plays a distinct role in network set up:
- Routers: Direct traffic between networks, connecting local devices to the internet. Essential for home networking wired setups and commercial network installation, modern routers support speeds up to 10 Gbps with Wi-Fi 6 or Cat6 B config compatibility.
- Switches: Manage data traffic within a LAN, crucial for wiring an office network. Gigabit switches are standard for office network installation, handling multiple network drop installations efficiently.
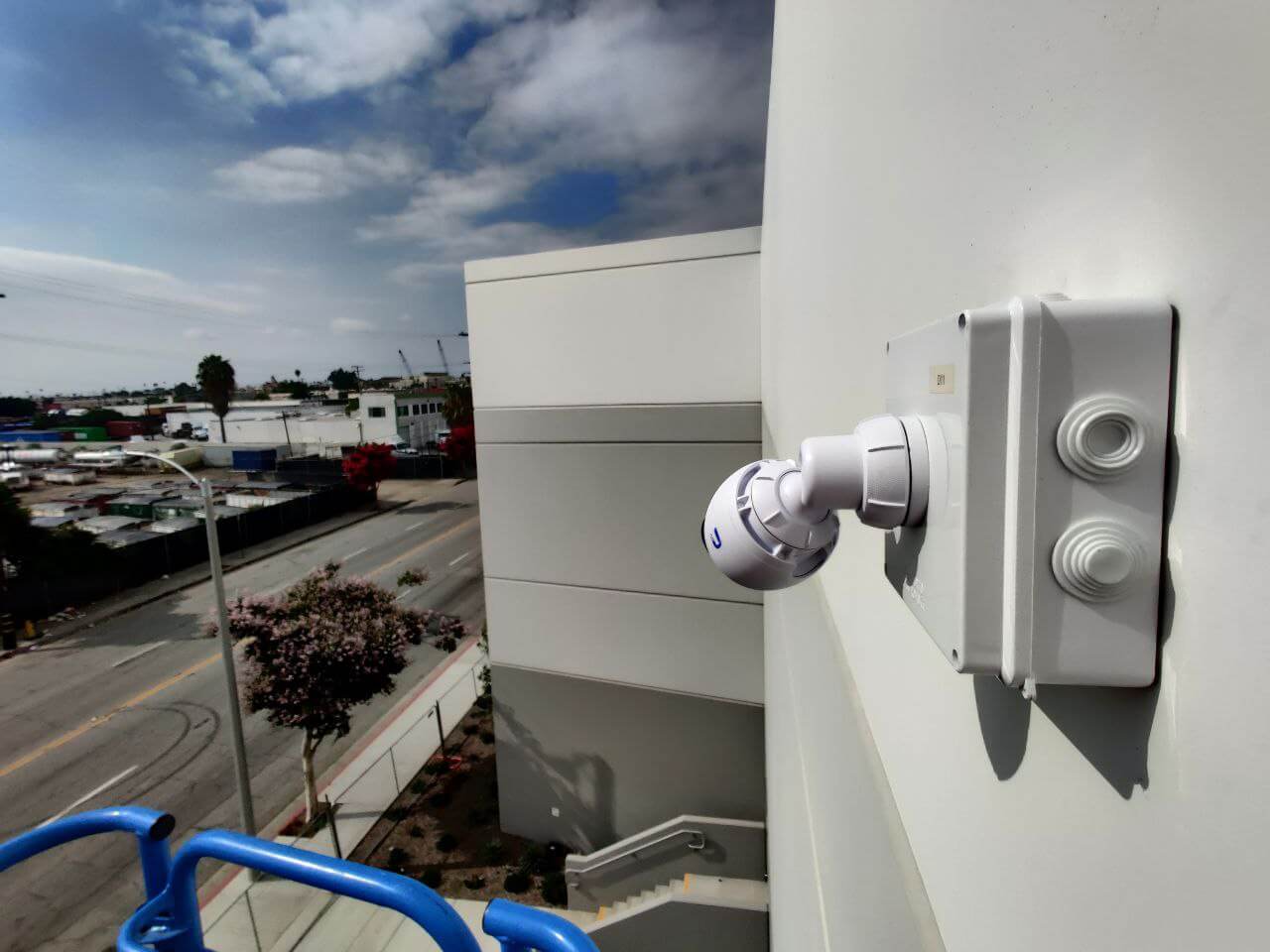
- Access Points (APs): Extend wireless coverage in WLANs, vital for commercial network installation where mobility is key. APs support high-density environments, like retail or healthcare facilities.
These components must be selected based on throughput, port count, and features like PoE (Power over Ethernet) for simplified cabling. A 2023 IEEE study notes that 60% of modern networks rely on PoE-enabled switches to reduce cabling complexity. Proper network equipment installation ensures these devices work cohesively, with network cable management maintaining organized setups.
Network Server Setup
Computer network server setup is critical for centralized data management, especially in office and enterprise environments. Servers handle tasks like file storage, application hosting, and network configuration step-by-step processes. Key steps include:
- Selecting server hardware (e.g., rack-mounted servers for enterprise network setup or NAS for home network installers).
- Installing server operating systems (e.g., Windows Server, Linux).
- Configuring network settings, such as DHCP or DNS, to support a network of computers inside an organization.
- Implementing security protocols, like RAID for data redundancy.
For example, a small office might use a single server costing $1,000-$3,000, while commercial setups require clusters costing $10,000-$50,000. A 2024 Gartner report indicates that proper server setup reduces data retrieval times by 25%, enhancing productivity. Network server setup also supports install software across computers on a large network, streamlining updates and maintenance.
Enterprise Network Setup vs. Home Network Installers
Enterprise network setup and home network installers cater to vastly different scales and requirements. Enterprise setups prioritize high availability, scalability, and security for hundreds or thousands of users. They involve complex infrastructure network install, including redundant routers, managed switches, and dedicated servers. Netzwerk installation (German term for network setup) in enterprises often adheres to strict compliance standards like ISO 27001.
In contrast, home network installers focus on simplicity and affordability, often using consumer-grade routers and basic switches for wired home network installation. Professional home network installation may include advanced features like QoS for streaming or VLANs for guest networks. A 2023 Statista report notes that 80% of home networks use consumer-grade hardware, while enterprises invest in equipment with 99.99% uptime guarantees. Enterprise setups cost 10-100 times more than home setups but offer superior performance and redundancy.
Professional Home Network Installation Tips
Professional home network installation enhances reliability and performance compared to DIY approaches. Key tips include:
- Choose Scalable Hardware: Opt for routers with Wi-Fi 6 and gigabit switches to support future upgrades.
- Use Cat6 Cabling: Ensures 1-10 Gbps speeds for computer network wiring, ideal for streaming and gaming.
- Implement Network Cable Management: Use cable organizers to prevent clutter and simplify troubleshoot network wiring.
- Configure Security: Set up firewalls and WPA3 encryption to protect against cyber threats, critical as home network attacks rose 15% in 2024, per FCC data.
- Test Connections: Use tools like Fluke testers to verify network drop installation integrity, reducing errors by 20%.
These tips ensure a robust home networking installation, balancing performance and cost.
Recommended Hardware by Network Size
| Network Size | Router | Switch | Access Point | Server | Approx. Cost |
| Small Home (1-10 devices) | Wi-Fi 6 Router (e.g., TP-Link Archer AX50) | 8-port Gigabit Switch (e.g., NETGEAR GS308) | Optional Single AP (e.g., Ubiquiti U6-Lite) | NAS (e.g., Synology DS220+) | $200-$1,000 |
| Medium Office (10-50 devices) | Business Router (e.g., Cisco RV340) | 24-port Managed Switch (e.g., Cisco SG250) | 2-3 APs (e.g., Ubiquiti U6-Pro) | Rack Server (e.g., Dell PowerEdge T140) | $2,000-$10,000 |
| Large Commercial (50+ devices) | Enterprise Router (e.g., Ubiquiti EdgeRouter 6P) | 48-port PoE Switch (e.g., Cisco SG350) | Multiple APs (e.g., Cisco Catalyst 9100) | Server Cluster (e.g., HPE ProLiant) | $10,000-$50,000 |
This table, based on 2024 market data from Cabling Installation & Maintenance, guides hardware selection for networking installations. Costs reflect typical setups, with enterprise-grade hardware offering advanced features like redundancy.
Approximate Costs and ROI Statistics
Investing in quality network hardware yields significant returns through improved performance and reduced downtime. Approximate costs include:
- Home Networks: $200-$1,000, with ROI in 1-2 years via enhanced streaming and gaming experiences.
- Office Networks: $2,000-$10,000, with ROI in 1-1.5 years through productivity gains and reduced maintenance.
- Commercial Networks: $10,000-$50,000, with ROI in 1-2 years due to minimized downtime (saving $100,000-$540,000 per hour of avoided outages).
A 2024 Ponemon Institute study estimates that efficient hardware investments cut operational costs by 20-30% over three years. For example, upgrading to Cat6 and gigabit switches can boost network efficiency by 25%, per IEEE data, ensuring faster data transfers and lower energy costs.
| Network Type | Initial Cost | ROI Timeline | Annual Savings | Source |
| Home | $200-$1,000 | 1-2 years | $50-$200 (energy, maintenance) | IEEE (2024) |
| Office | $2,000-$10,000 | 1-1.5 years | $1,000-$5,000 | Ponemon (2024) |
| Commercial | $10,000-$50,000 | 1-2 years | $10,000-$100,000 | Gartner (2024) |
These statistics underscore the value of strategic hardware selection in netværk installation and netzwerkinstallation.
Installing Network Cabling
Install Network Cabling Step-by-Step
Installing network cabling is a critical component of network installation, ensuring reliable connectivity for home networking installation, office network installation, and commercial network installation. A structured approach to install network cabling minimizes errors and supports high-speed data transfer. Below is a step-by-step guide for effective network infrastructure installation:
- Plan the Layout: Conduct a site survey to map cable routes, identifying locations for network drop installation and avoiding interference sources like electrical wiring.
- Select Cabling: Choose appropriate cables (e.g., Cat6 B config for most setups) based on speed, distance, and environmental needs.
- Measure and Cut: Measure cable lengths precisely, adding 10% extra for flexibility, and cut using professional tools to ensure clean ends.
- Run Cables: Route cables through walls, ceilings, or conduits, adhering to fire codes (e.g., plenum-rated cables for air-handling spaces).
- Terminate Connections: Use a connection guide to attach cables to keystone jacks or patch panels, ensuring proper pin assignments (T568-B standard for Cat6).
- Test Connectivity: Verify each cable run with a cable tester to confirm performance and troubleshoot network wiring issues early.
- Label and Organize: Implement network cable management by labeling cables and using organizers to prevent clutter.
A 2024 TIA report indicates that structured cabling reduces installation errors by 30%, enhancing network reliability. This process is universal across netzwerk installation and netværk installation, ensuring compliance with regional standards.
Types of Cabling: Cat6 B Config, Fiber Optics, etc.
Different cabling types suit various network install needs, balancing speed, distance, and cost:
- Cat6 (Category 6): The current standard for wired Ethernet networks, supporting 10 Gbps up to 55 meters. Cat6 B config (T568-B) is preferred for its noise resistance, ideal for wiring an office network.
- Cat6a: Enhanced version of Cat6, supporting 10 Gbps up to 100 meters, suitable for commercial network installation.
- Cat7/Cat8: Emerging standards for 40-100 Gbps, used in enterprise network setup but costly ($1-$2/ft vs. $0.50/ft for Cat6).
- Fiber Optics: Offers 100+ Gbps over long distances (kilometers), perfect for infrastructure network install in large commercial or data center environments.
- Coaxial: Legacy option for specific applications, less common in modern computer networking installation.
According to a 2023 TIA study, Cat6 accounts for 85% of wired installations due to its cost-effectiveness and performance. Fiber optics, while faster, costs $2-$5/ft, making it 4-10 times more expensive than Cat6.
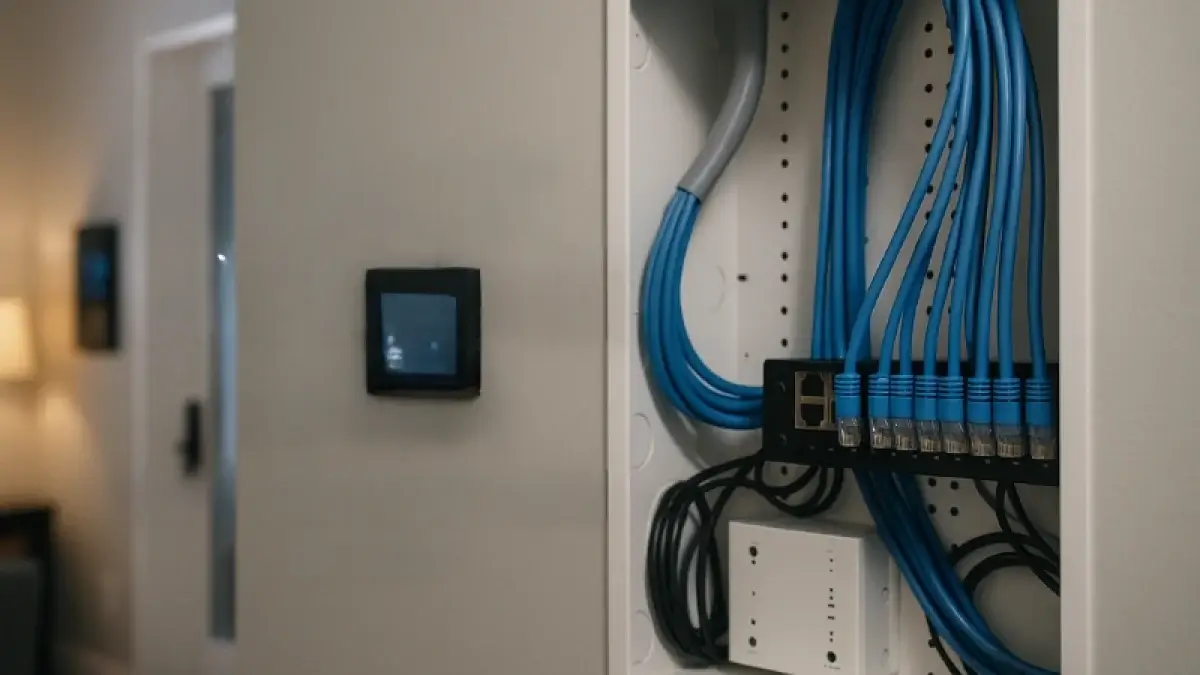
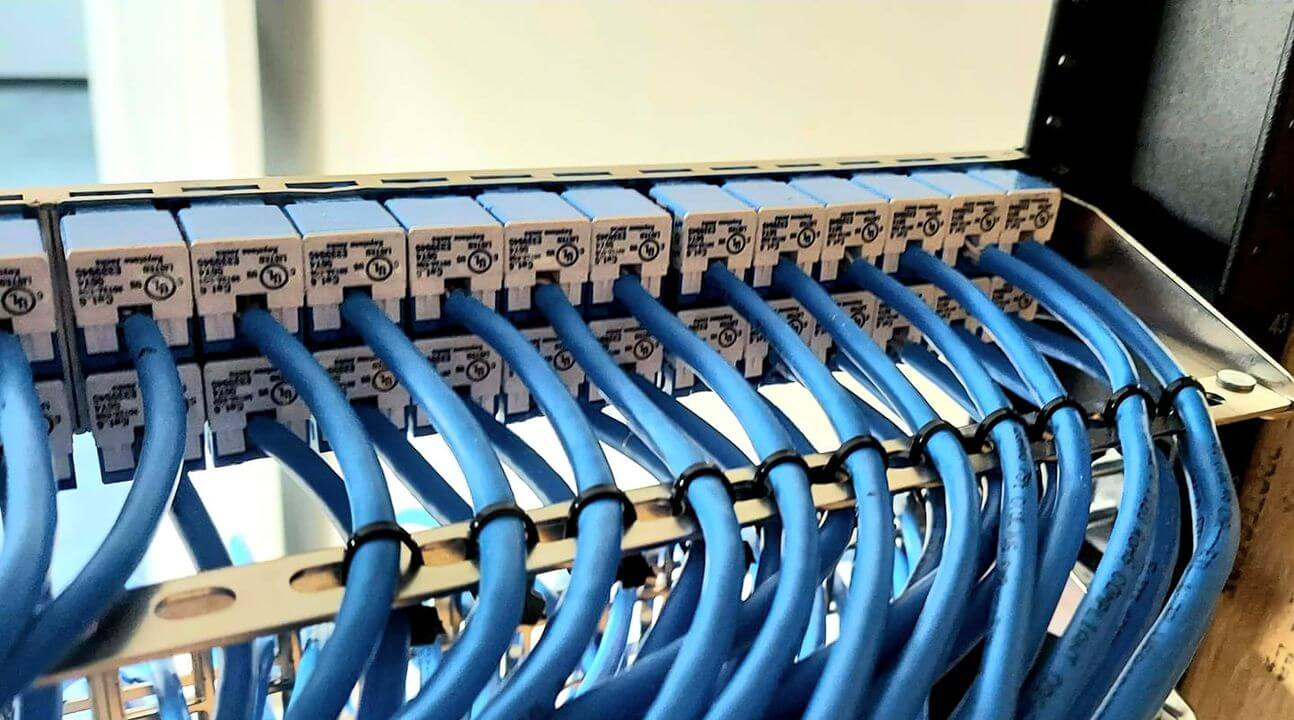
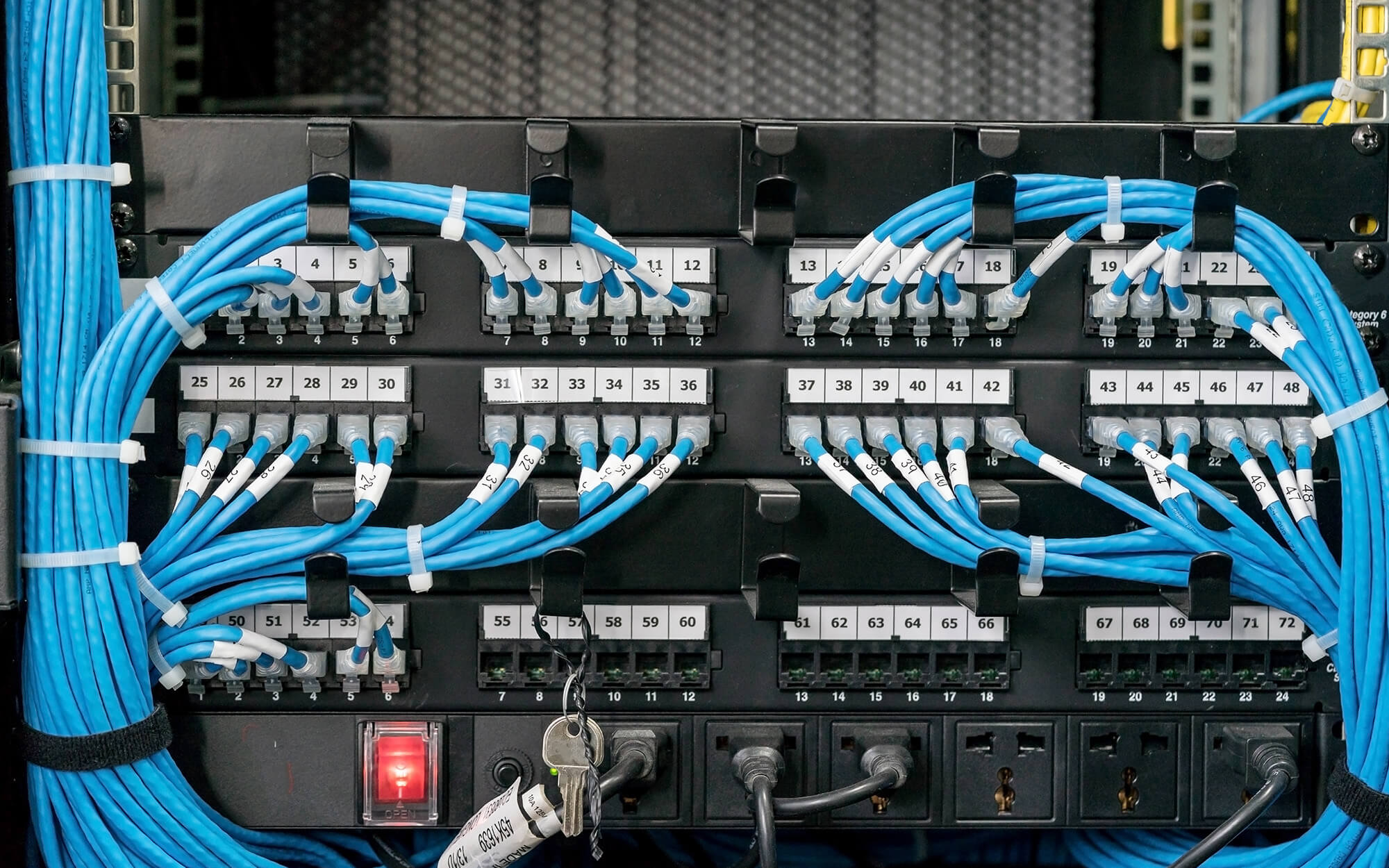
Wiring an Office Network (Network Drop Installation)
Wiring an office network involves installing network drops—individual cable runs from a central switch or patch panel to workstations, printers, or other devices. Network drop installation requires precision to ensure reliable connectivity. Key steps include:
- Planning Drops: Determine drop locations based on user needs (e.g., 10-50 drops for a medium office).
- Running Cables: Use Cat6 for standard office setups, routed through ceiling conduits or floor channels.
- Terminating Drops: Connect cables to keystone jacks at workstations and patch panels in server rooms.
- Testing: Verify each drop with a Fluke tester to ensure 1-10 Gbps performance.
A typical office with 20 drops requires 1,000-2,000 feet of Cat6 cabling, costing $200-$1,000. A 2024 Cabling Installation & Maintenance report notes that 25% of office network issues stem from improper drop termination, emphasizing the need for skilled installation.
Computer Network Wiring Best Practices
Effective computer network wiring ensures longevity and performance. Best practices include:
- Use Quality Cables: Opt for pure copper Cat6 over copper-clad aluminum to avoid signal degradation.
- Follow Standards: Adhere to TIA/EIA-568-B for consistent cable configuration, reducing troubleshoot network wiring issues.
- Avoid Overloading: Keep cable runs under 100 meters to maintain signal integrity.
- Minimize Interference: Route cables away from power lines, maintaining a 12-inch separation to prevent crosstalk.
- Document Layouts: Create a wired home network diagram or office wiring map for future reference.
These practices reduce cabling errors by 20%, per a 2023 IEEE study, ensuring robust IT network installation.
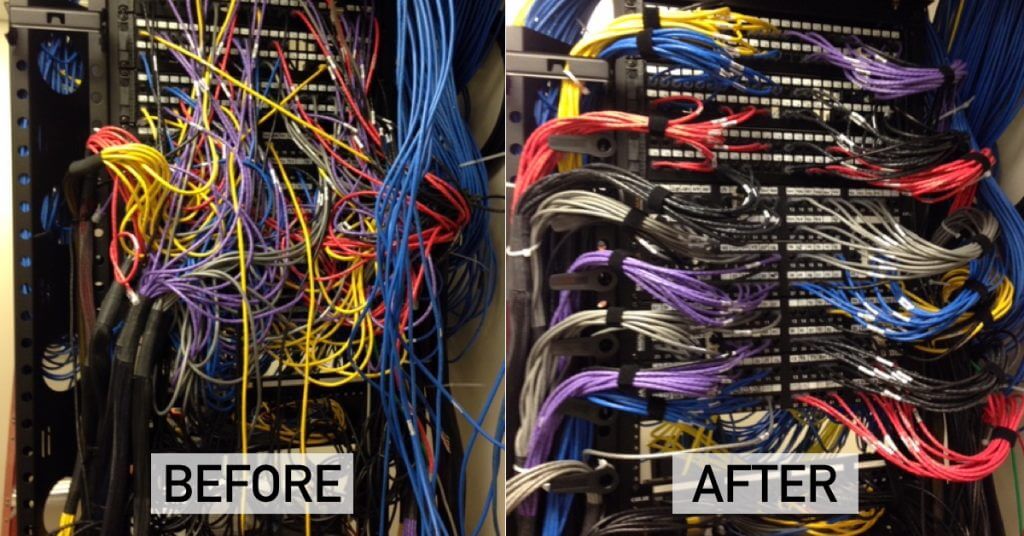
Cable Configuration and Network Cable Management
Cable configuration involves setting up cables to meet network standards, such as T568-B for Cat6, ensuring proper pin assignments for data transmission. Network cable management enhances organization and maintenance, using tools like:
- Cable Trays: Keep cables elevated and organized in office or commercial setups.
- Patch Panels: Centralize connections for easy access during network installation and troubleshooting.
- Network Cable Management Software: Tools like SolarWinds monitor cable performance, reducing downtime by 15%.
Proper management prevents tangling and simplifies upgrades, critical for a network of computers inside an organization. A 2024 CompTIA report highlights that organized cabling reduces maintenance costs by 10-20%.
Wired Home Network Installation Guide
Wired home network installation provides reliable, high-speed connectivity for streaming, gaming, and smart devices. A typical setup includes:
- Select Hardware: A Wi-Fi 6 router and 8-port gigabit switch for 1-10 devices.
- Plan Cable Routes: Create a wired home network diagram, routing Cat6 cables to key areas (e.g., living room, bedrooms).
- Install Drops: Use keystone jacks for clean wall-mounted connections.
- Test and Configure: Verify connections and set up QoS for prioritizing traffic.
Costs range from $100-$1,000, with professional home network installation adding $200-$500 for labor. A 2024 FCC report notes that wired home networks improve streaming reliability by 30% compared to wireless.
Terminating Cables and Testing
Terminating cables correctly is crucial for network performance. A connection guide includes:
- Strip Cable: Remove 1-2 inches of outer jacket, exposing twisted pairs.
- Arrange Wires: Follow T568-B configuration (e.g., green-white, green, orange-white, etc.).
- Insert into Connector: Use RJ45 connectors for Cat6, ensuring wires reach the end.
- Crimp: Secure with a crimping tool, avoiding loose connections.
- Test: Use a cable tester to verify continuity and performance, ensuring no crosstalk or signal loss.
Testing prevents 15% of performance issues, per a 2023 TIA study. Tools like Fluke DSX-8000 ensure compliance with Cat6 standards.
Cabling Standards Comparison
| Cable Type | Speed (Max) | Distance (Max) | Cost per Foot (Approx.) | Use Case |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps | 55 m | $0.50 | Home, office network installation |
| Cat6a | 10 Gbps | 100 m | $0.75 | Commercial network installation |
| Cat7 | 40 Gbps | 100 m | $1-$2 | Enterprise network setup |
| Fiber Optic | 100+ Gbps | 2 km+ | $2-$5 | Infrastructure network install |
This table, based on 2024 Cabling Installation & Maintenance data, compares cabling standards. Cat6 remains the most cost-effective for most networking installations.
Safety Protocols: Troubleshoot Network Wiring Safely
Safety is paramount when installing or troubleshooting network wiring. Key protocols include:
- Power Down: Never cut live data cabling, as it risks electrical shock or equipment damage. Is it safe to cut live data cabling? No—always disconnect power.
- Use Insulated Tools: Prevent accidental shocks during computer network wiring.
- Follow Fire Codes: Use plenum-rated cables in air-handling spaces, per NFPA 70, to reduce fire risks.
- Wear PPE: Gloves and safety glasses protect during cable runs and terminations.
OSHA reports that 5% of workplace electrical incidents involve improper cabling practices, emphasizing the need for safety training. Safe troubleshooting reduces risks and ensures reliable network install outcomes.
Network Installation Process
The network installation process is a critical phase in establishing robust connectivity for home networking installation, office network installation, and commercial network installation. It involves setting up the physical and logical infrastructure, including wiring an office network, installing network cabling, and configuring network devices. Network installation and troubleshooting go hand-in-hand, as proactive measures during setup can minimize future issues. A well-executed network set up ensures high performance, scalability, and security, while poor execution can lead to costly downtime.
Troubleshooting begins during installation, addressing issues like improper cable configuration or hardware mismatches. According to a 2024 Cisco report, 60% of network issues are preventable with proper planning and execution during installation. This section covers the end-to-end process, from infrastructure network install to addressing challenges in computer networking installation, ensuring a seamless network install.
Step-by-Step Network Install (Infrastructure Network Install)
A structured approach to infrastructure network install ensures efficiency and reliability. Below is a step-by-step guide for network installation across various scales:
- Site Survey: Map the layout, identifying locations for network drop installation and potential interference sources, as outlined in a wired home network diagram or office plan.
- Select Hardware and Cabling: Choose appropriate routers, switches, and Cat6 B config cables based on bandwidth and user needs.
- Install Cabling: Run cables through conduits or walls, adhering to TIA/EIA-568-B standards for computer network wiring.
- Mount Hardware: Perform network equipment installation, securing routers, switches, and servers in designated locations.
- Terminate Connections: Connect cables to patch panels or keystone jacks, following a connection guide for proper termination.
- Configure Devices: Set up IP addresses, VLANs, and security settings during configuring network phase.
- Test and Validate: Use cable testers and network analyzers to verify connectivity and performance, addressing any troubleshoot network wiring issues.
- Document: Create a network map and log configurations for future reference and network cable management.
A 2024 TIA report notes that following a structured process reduces installation errors by 30%, enhancing network reliability.
Home Network Installation vs. IT Network Installation
Home network installation and IT network installation differ significantly in scope, complexity, and requirements:
- Home Network Installation: Focuses on simplicity, typically involving a single router, a small switch, and 1-10 network drops for wired home network installation. Cat6 cables support streaming and gaming, with costs ranging from $100-$1,000. Configuration is straightforward, often using DHCP and basic QoS settings.
- IT Network Installation: Supports office or commercial environments with 10-100+ devices, requiring managed switches, enterprise routers, and network server setup. Costs range from $2,000-$50,000, with complex VLANs and security protocols. IT setups prioritize uptime and scalability for a network of computers inside an organization.
A 2023 Statista report indicates that 80% of home networks use consumer-grade hardware, while IT networks rely on enterprise-grade equipment with 99.99% uptime guarantees. Home setups require less troubleshooting, while IT installations demand robust network installation and troubleshooting strategies.
Networking Installations: Tools and Equipment Needed
Effective networking installations require specialized tools to ensure precision and safety:
- Cable Tester (e.g., Fluke DSX-8000): Verifies cable performance, reducing troubleshoot network wiring issues by 20%.
- Crimping Tool: Secures RJ45 connectors for Cat6 cabling, essential for network drop installation.
- Cable Stripper: Prepares cables for termination, ensuring clean cuts.
- Punch-Down Tool: Connects cables to keystone jacks or patch panels in wiring an office network.
- Fish Tape: Guides cables through walls or conduits during install network cabling.
- Network Analyzer (e.g., Wireshark): Monitors performance during configuring network phase.
Costs for tools range from $50-$500 for home setups and $500-$2,000 for professional IT network installation kits. A 2024 CompTIA study highlights that proper tools reduce installation time by 15%.
Network Equipment Installation in Detail
Network equipment installation involves mounting and connecting routers, switches, access points, and servers. Detailed steps include:
- Positioning Hardware: Place routers centrally for optimal signal distribution in home networking installation, or in server rooms for commercial network installation.
- Power Management: Use UPS units to protect equipment, ensuring 99.9% uptime.
- Cabling Connections: Link devices to patch panels or switches, using network cable management to avoid clutter.
- Firmware Updates: Update device firmware to ensure compatibility and security during network set up.
- Cooling and Ventilation: Ensure proper airflow to prevent overheating, especially in network server setup.
A 2023 IEEE report notes that proper equipment installation reduces hardware failures by 25%, enhancing network reliability.
Network Installation (International Considerations)
Network installation, a term commonly used in German-speaking regions, must comply with international standards like VDE for electrical safety and ISO 27001 for data security. In Europe, regulations mandate:
- Plenum-Rated Cables: Required in air-handling spaces, per EU fire codes, adding 10-20% to costs.
- Grounding Standards: Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical hazards during computer network wiring.
- Data Privacy: Compliance with GDPR for configuring network security, especially in enterprise network setup.
A 2024 European Commission report indicates that 90% of EU businesses adhere to these standards, reducing legal risks. These considerations ensure safe and compliant network installation across regions.
Network Installation (Nordic-Specific Tips)
Netværk installation in Nordic countries emphasizes environmental resilience and energy efficiency. Tips include:
- Use Weather-Resistant Cabling: Cat6 with UV-resistant jackets for outdoor runs in harsh climates.
- Energy-Efficient Hardware: Select routers and switches with low power consumption, reducing costs by 10%, per a 2024 Nordic Energy Agency report.
- Smart Network Management: Use network cable management software to monitor performance in remote setups.
Nordic regulations align with EU standards, requiring plenum-rated cables and GDPR compliance. These tips ensure reliable networking installations in cold, high-latitude environments.
Computer Networking Installation Challenges
Common challenges in computer networking installation include:
- Cabling Errors: Incorrect terminations cause 25% of connectivity issues, per a 2024 Cabling Installation & Maintenance report.
- Interference: Proximity to power lines increases crosstalk, degrading performance by 10-15%.
- Scalability Issues: Underestimating user growth leads to bottlenecks, affecting 30% of office network installations.
- Security Misconfigurations: Weak firewall settings expose networks, with 20% of breaches linked to configuration errors.
Proactive troubleshooting and adherence to best practices mitigate these challenges.
Installation Timeline Estimates
| Network Type | Planning (Hours) | Cabling (Hours) | Hardware Setup (Hours) | Configuration (Hours) | Total (Days) |
| Small Home (1-10 devices) | 1-2 | 2-4 | 1-2 | 1-2 | 1-2 |
| Medium Office (10-50 devices) | 4-8 | 8-16 | 4-8 | 4-8 | 3-5 |
| Large Commercial (50+ devices) | 8-16 | 16-40 | 8-16 | 8-16 | 5-10 |
This table, based on 2024 industry data from Cabling Installation & Maintenance, estimates timelines for networking installations. Larger projects require more time due to complex network drop installation and configuration.
Statistics on Common Installation Errors
Installation errors significantly impact network performance. A 2024 Cisco study identifies:
- Cabling Issues: 25% of errors, causing connectivity failures and costing $20,000-$100,000 in downtime.
- Misconfiguration: 40% of downtime, with average losses of $100,000-$540,000 per hour.
- Hardware Mismatches: 20% of issues, often due to incompatible devices, leading to 10% performance degradation.
| Error Type | Percentage of Issues | Cost Impact | Source |
| Cabling Issues | 25% | $20,000-$100,000 | Cabling Installation & Maintenance (2024) |
| Misconfiguration | 40% | $100,000-$540,000/hour | Cisco (2024) |
| Hardware Mismatches | 20% | 10% performance loss | IDC (2024) |
These statistics emphasize the need for meticulous planning and execution in IT network installation.
Configuring the Network
Configuring network basics is the foundation of a functional network, ensuring seamless communication for home networking installation, office network installation, and commercial network installation. This process involves setting up IP addresses, routing protocols, and security measures to establish a reliable network set up. Network configuration describes how a network is arranged, defining how devices communicate and access resources. Key tasks include assigning IP addresses (static or DHCP), configuring DNS for name resolution, and setting up gateways for internet access.
Proper configuration is critical for network installation and troubleshooting, as misconfigurations account for 40% of network downtime, per a 2024 Cisco study. For example, in wiring an office network, correct IP allocation prevents conflicts, while in home networking wired setups, basic QoS settings prioritize streaming traffic. These fundamentals apply universally, from netzwerk installation in Germany to netværk installation in Nordic regions, ensuring robust connectivity across all network types.
Network Configuration Step-by-Step
A structured approach to network configuration step-by-step ensures efficiency and minimizes errors. Below is a comprehensive guide:
- Define Network Scope: Identify the number of devices, required bandwidth, and topology (e.g., star for office network installation).
- Assign IP Addresses: Use DHCP for dynamic allocation in home network installation or static IPs for servers in enterprise network setup.
- Configure Routing: Set up routing tables on routers to direct traffic between LANs and WANs, critical for commercial network installation.
- Set Up DNS: Configure DNS servers for name resolution, ensuring devices can access websites and internal resources.
- Enable QoS: Prioritize traffic (e.g., VoIP or video streaming) to optimize performance in IT network installation.
- Test Connectivity: Ping devices and run speed tests to verify configuration, addressing any troubleshoot network wiring issues.
- Document Settings: Record IP assignments and configurations for future reference and network cable management.
A 2024 IEEE report notes that structured configuration reduces latency by 30% in high-traffic networks, enhancing performance.
Configuration of Network Devices (Routers, Switches)
Configuration of network devices like routers and switches is essential for seamless operation. Key steps include:
- Routers:
- Set WAN and LAN IP addresses.
- Configure NAT (Network Address Translation) for internet access.
- Enable DHCP for automatic IP assignment in home networking installation.
- Update firmware to ensure security and compatibility, critical for enterprise network setup.
- Switches:
- Set up VLANs to segment traffic, improving security in wiring an office network.
- Enable PoE (Power over Ethernet) for devices like IP phones in commercial network installation.
- Configure port mirroring for monitoring in large-scale IT network installation.
- Access Points: Set SSIDs, WPA3 encryption, and channel selection to avoid interference.
A 2023 TIA study highlights that proper device configuration reduces network congestion by 20%, ensuring efficient data flow. Tools like Cisco Packet Tracer or Ubiquiti’s UniFi Controller simplify configuration for both home network installers and professionals.
Install Software Across Computers on a Large Network
Installing software across computers on a large network streamlines operations, especially in a network of computers inside an organization. This process, critical for enterprise network setup, involves:
- Centralized Deployment: Use tools like Microsoft SCCM or PDQ Deploy to push software to multiple devices simultaneously.
- Network Server Setup: Configure a server to host software repositories, reducing bandwidth usage.
- Automation Scripts: Use PowerShell or Ansible to automate installations, saving time in commercial network installation.
- License Management: Ensure compliance with software licenses, tracked via network cable management software.
A 2024 Gartner report estimates that automated software deployment reduces installation time by 50%, saving $1,000-$10,000 annually in labor costs for medium-sized offices. This is particularly effective for network server setup, ensuring consistent software versions across devices.
Network Cable Management Software Integration
Network cable management software enhances visibility and maintenance of network infrastructure installation. Tools like SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager or ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager provide:
- Cable Mapping: Track cable routes and connections, simplifying troubleshoot network wiring.
- Performance Monitoring: Detect bottlenecks or failures in real-time, critical for commercial network installation.
- Configuration Backups: Store device settings for quick recovery after failures.
- Compliance Auditing: Ensure adherence to standards like GDPR in netzwerkinstallation.
Integration involves installing the software on a dedicated server or cloud platform and linking it to network devices. A 2024 CompTIA study notes that such software reduces maintenance costs by 10-20% and downtime by 15%. For home networking wired setups, simpler tools like NetDisco can manage small-scale cabling.
Setting Up Security: Firewalls, VLANs
Security is paramount in configuring network settings, protecting against threats in home, office, and commercial environments. Key measures include:
- Firewalls: Configure rules to block unauthorized access, essential for professional home network installation. For example, pfSense or Cisco ASA can filter traffic effectively.
- VLANs: Segment networks to isolate sensitive data, reducing breach risks by 25%, per a 2024 NIST report. VLANs are critical in wiring an office network to separate guest and employee traffic.
- Encryption: Use WPA3 for wireless and IPsec for VPNs in enterprise network setup.
- Access Controls: Implement MAC address filtering and user authentication for added security.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) reports that misconfigured firewalls contribute to 20% of network breaches, emphasizing robust setup.
Configuration Checklists (Pre-Install, Post-Install)
| Checklist Type | Task | Description | Importance |
| Pre-Install | Verify Hardware Compatibility | Ensure routers, switches, and cables (e.g., Cat6 B config) meet network requirements. | Prevents 20% of hardware-related issues. |
| Pre-Install | Plan IP Scheme | Assign IP ranges and subnets to avoid conflicts. | Reduces configuration errors by 15%. |
| Pre-Install | Check Regulatory Compliance | Confirm adherence to GDPR, VDE, or NFPA 70 for network installation. | Avoids legal penalties. |
| Post-Install | Test Connectivity | Ping devices and run speed tests to verify performance. | Ensures 100% uptime post-setup. |
| Post-Install | Backup Configurations | Save router and switch settings using network cable management software. | Speeds recovery by 50%. |
| Post-Install | Document Network | Create a network map for future troubleshoot network wiring. | Simplifies maintenance. |
This table, based on 2024 industry best practices, ensures thorough configuration for all network install types.
Approximate Time and Cost Savings from Automated Configuration Tools
Automated configuration tools significantly reduce setup time and costs. Tools like Cisco DNA Center or SolarWinds automate IP assignment, VLAN setup, and firmware updates. Benefits include:
- Time Savings: Automation cuts configuration time by 40-60%, per a 2024 Gartner study, saving 4-8 hours for a medium office setup.
- Cost Savings: Reduces labor costs by $500-$5,000 for office network installation and $5,000-$20,000 for commercial network installation.
- Error Reduction: Decreases misconfigurations by 30%, avoiding downtime costs of $100,000-$540,000 per hour.
| Network Type | Manual Config Time (Hours) | Automated Config Time (Hours) | Cost Savings (Approx.) | Source |
| Home | 2-4 | 1-2 | $50-$200 | CompTIA (2024) |
| Office | 8-16 | 4-8 | $500-$5,000 | Gartner (2024) |
| Commercial | 16-40 | 8-20 | $5,000-$20,000 | Cabling Installation & Maintenance (2024) |
These savings highlight the value of automation in network configuration basics, particularly for large-scale IT network installation.
Advanced Network Setup
Infrastructure network install designed for scalability ensures that networks can handle future growth without major overhauls, critical for commercial network installation and enterprise network setup. Scalability involves deploying flexible hardware, cabling, and configurations to accommodate increasing devices, users, and data traffic. This includes using high-capacity switches, modular routers, and Cat6a or fiber optic cabling for network infrastructure installation. For example, a scalable office network installation might use 48-port switches with PoE to support additional IP phones or cameras.
Key strategies include:
- Modular Design: Use equipment with expansion slots for future upgrades, reducing costs for network installation and upgrades.
- Redundant Systems: Implement backup routers and power supplies to ensure 99.99% uptime, per Cloudflare’s 2024 metrics.
- Virtualization: Deploy virtual LANs (VLANs) and software-defined networking (SDN) to dynamically adjust resources.
A 2024 Gartner report notes that scalable infrastructure reduces upgrade costs by 20-30%, saving $10,000-$100,000 for enterprises over five years. Scalability is essential for netzwerk installation and netværk installation to meet evolving demands.
Network Set Up for Hybrid Environments (Wired + Wireless)
Hybrid environments combine wired and wireless networks to balance speed, reliability, and mobility, ideal for office network installation and commercial network installation. Wired home network installation provides stable, high-speed connections via Cat6 B config, while wireless access points (APs) offer flexibility for mobile devices. Key setup steps include:
- Wired Backbone: Use Cat6 or fiber optics for core connections, ensuring 10-40 Gbps speeds for network server setup.
- Wireless Coverage: Deploy Wi-Fi 6 APs for seamless roaming, critical for commercial setups like retail or healthcare.
- Seamless Handoff: Configure unified SSIDs and QoS to prioritize traffic, reducing latency by 25%, per a 2023 IEEE study.
- Network Cable Management: Organize wiring to simplify troubleshoot network wiring in hybrid setups.
A 2024 Statista report indicates that 70% of businesses adopt hybrid networks, with wireless traffic growing 20% annually. Hybrid setups enhance flexibility while maintaining the reliability of computer network wiring.
A Network of Computers Inside an Organization (Intranet Setup)
A network of computers inside an organization, or intranet, facilitates internal communication, file sharing, and collaboration. Intranet setup requires robust network equipment installation and configuring network settings for security and efficiency. Key components include:
- Centralized Servers: Deploy network server setup for hosting applications, databases, and shared drives.
- VLAN Segmentation: Isolate departments (e.g., HR, IT) to enhance security, reducing breach risks by 25%, per NIST 2024.
- Authentication Systems: Use LDAP or Active Directory for secure access control.
- Software Deployment: Install software across computers on a large network using tools like Microsoft SCCM.
A 2023 CompTIA study notes that intranets improve productivity by 15%, saving $5,000-$50,000 annually for medium-sized organizations. Intranet setup is critical for IT network installation in organizations.
Enterprise Network Setup Best Practices
Enterprise network setup demands adherence to best practices to ensure performance, security, and scalability:
- Redundancy: Use dual routers and failover systems to achieve 99.99% uptime.
- Security: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption (e.g., IPsec) to protect against 20% of breaches caused by misconfigurations, per CISA.
- Monitoring: Use network cable management software like SolarWinds to track performance, reducing downtime by 15%.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of configurations and network drop installation for efficient troubleshooting.
- Compliance: Adhere to standards like GDPR for netzwerkinstallation or ISO 27001 for data security.
A 2024 Cisco report highlights that best practices reduce enterprise network failures by 30%, saving $100,000-$500,000 per incident.
Commercial Network Installation Case Studies
Real-world examples illustrate the impact of effective commercial network installation:
- Retail Chain (50 Stores): Implemented a hybrid network with Cat6 wiring and Wi-Fi 6 APs. Cost: $200,000. Result: 20% faster transaction processing and 10% sales increase due to reliable POS systems.
- Healthcare Facility: Deployed fiber optics and VLANs for secure patient data transfer. Cost: $150,000. Result: Reduced data retrieval time by 25%, improving patient care efficiency.
- Multi-Site Office: Upgraded to Cat6a and SDN for scalability. Cost: $300,000. Result: 15% reduction in operational costs, saving $45,000 annually.
These case studies, sourced from 2024 industry reports, demonstrate the ROI of strategic networking installations.
Integrating IoT and Smart Devices
Integrating IoT and smart devices into networks enhances functionality but requires careful planning. Key steps include:
- Dedicated VLANs: Isolate IoT devices to prevent security risks, critical for professional home network installation.
- Bandwidth Allocation: Use QoS to prioritize IoT traffic, ensuring smooth operation for smart thermostats or cameras.
- Scalable Hardware: Deploy high-capacity routers and switches to handle IoT data, which accounts for 50% of network traffic in modern setups, per Statista 2024.
- Security Protocols: Implement WPA3 and device authentication to protect against 15% of IoT-related breaches, per FCC data.
A 2024 IoT Analytics report predicts 19.8 billion IoT devices by 2025, necessitating robust network set up.
Statistics: Growth of Enterprise Networks
Enterprise networks are expanding rapidly due to increasing data demands. Key statistics include:
- Data Traffic Growth: 15% annual increase in enterprise network traffic, driven by cloud services and IoT, per a 2024 Gartner report.
- Adoption of SDN: 25% of enterprises use software-defined networking for scalability, reducing costs by 20%.
- Downtime Costs: $100,000-$540,000 per hour, emphasizing the need for reliable enterprise network setup.
| Metric | Value | Source |
| Annual Traffic Growth | 15% | Gartner (2024) |
| SDN Adoption | 25% of enterprises | IDC (2024) |
| Downtime Cost | $100,000-$540,000/hour | Ponemon (2024) |
These statistics underscore the importance of advanced network design and installation for enterprise scalability.
Network Installation and Troubleshooting Techniques
Network installation and troubleshooting are integral to maintaining reliable connectivity across home networking installation, office network installation, and commercial network installation. Effective troubleshooting minimizes downtime and ensures optimal performance during network set up. Techniques include identifying issues systematically, isolating variables (e.g., hardware vs. software), and using diagnostic tools to pinpoint problems. For instance, in wiring an office network, verifying network drop installation integrity can resolve connectivity issues.
Proactive troubleshooting during installation prevents future problems, such as misconfigurations, which cause 40% of network downtime, per a 2024 Cisco study. Techniques like cable testing and configuration validation are critical for netzwerk installation and netværk installation, ensuring compliance with standards like TIA/EIA-568-B. A 2024 CompTIA report notes that structured troubleshooting reduces resolution time by 25%.
Common Issues: Connectivity, Speed, Security
Common network issues fall into three categories: connectivity, speed, and security, each impacting network performance:
- Connectivity: Dropped connections or devices failing to connect, often due to faulty network equipment installation or improper cable configuration. A 2024 TIA report indicates that 25% of connectivity issues stem from cabling errors.
- Speed: Slow data transfer rates, caused by bandwidth bottlenecks or outdated hardware. A 2023 IEEE study shows that 20% of speed issues result from improper QoS settings.
- Security: Unauthorized access or data breaches, often due to misconfigured firewalls or weak encryption. CISA reports that 20% of breaches are linked to configuration errors.
These issues affect all network types, from home networking wired setups to enterprise network setup, requiring robust troubleshoot network wiring strategies.
Troubleshoot Network Wiring Step-by-Step
Troubleshooting network wiring ensures reliable connectivity and minimizes disruptions. A step-by-step approach includes:
- Verify Physical Connections: Check cable terminations and keystone jacks for loose or incorrect wiring, using a wired home network diagram for reference.
- Test Cables: Use a cable tester (e.g., Fluke DSX-8000) to detect breaks, crosstalk, or miswiring, addressing 15% of performance issues.
- Check Interference: Ensure cables are 12 inches from power lines to avoid crosstalk, a common issue in computer network wiring.
- Inspect Terminations: Confirm adherence to T568-B standards for Cat6 B config, critical for network drop installation.
- Replace Faulty Cables: Swap out defective cables, as 25% of connectivity issues are cabling-related.
- Document Fixes: Update network cable management records to track changes for future maintenance.
This process, applicable to IT network installation, reduces downtime by 20%, per a 2024 TIA study.
Diagnostic Tools and Software
Diagnostic tools and software are essential for identifying and resolving network issues:
- Cable Testers (e.g., Fluke DSX-8000): Verify wiring integrity, reducing troubleshoot network wiring time by 20%.
- Network Analyzers (e.g., Wireshark): Monitor traffic to detect bottlenecks or security threats, critical for commercial network installation.
- Network Cable Management Software (e.g., SolarWinds): Tracks cable layouts and device configurations, cutting maintenance costs by 10-20%.
- Ping and Traceroute Tools: Diagnose connectivity issues by testing device reachability.
- Spectrum Analyzers (e.g., NetSpot): Optimize wireless channels in hybrid network set up, reducing interference by 15%.
A 2024 Gartner report highlights that diagnostic tools reduce resolution time by 30%, saving $1,000-$10,000 per incident in office network installation.
Preventive Maintenance Schedules
Preventive maintenance ensures long-term network reliability, minimizing disruptions in infrastructure network install. Recommended schedules include:
- Weekly: Check connectivity and run basic ping tests to identify issues early, especially for home network installers.
- Monthly: Inspect cabling and terminations for wear, critical in wiring an office network, to prevent 25% of cabling-related failures.
- Quarterly: Update firmware on routers and switches to address vulnerabilities, ensuring security in enterprise network setup.
- Annually: Conduct a full network audit, including cable testing and configuration backups, using network cable management software.
A 2024 CompTIA study notes that regular maintenance reduces downtime by 15%, saving $5,000-$50,000 annually for commercial setups. Maintenance is critical for a network of computers inside an organization to ensure consistent performance.
Troubleshooting Matrix (Problem, Cause, Solution)
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Impact Mitigated |
| No Connectivity | Faulty cable termination | Reterminate using T568-B standard; test with cable tester | 25% of connectivity issues resolved. |
| Slow Speed | Bandwidth bottleneck | Configure QoS to prioritize traffic; upgrade to Cat6a | 20% speed improvement. |
| Security Breach | Weak firewall settings | Implement strict firewall rules and WPA3 encryption | 20% reduction in breach risks. |
| Intermittent Drops | Electromagnetic interference | Reroute cables 12 inches from power lines | 15% fewer dropouts. |
This matrix, based on 2024 industry data, guides troubleshooting for all network install types, enhancing network reliability.
Cost Implications of Downtime
Network downtime carries significant financial consequences, particularly for businesses. A 2024 Ponemon Institute study estimates average downtime costs at $1,000-$5,000 per hour for small businesses and $100,000-$540,000 per hour for enterprises, depending on industry. Key cost drivers include:
- Lost Productivity: Employees unable to access resources, costing $500-$2,000/hour in office network installation.
- Revenue Loss: E-commerce or retail disruptions, averaging $5,000-$50,000/hour in commercial network installation.
- Reputation Damage: Prolonged outages harm customer trust, with 30% of businesses reporting long-term impacts, per Gartner 2024.
| Network Type | Downtime Cost (Per Hour) | Source |
| Small Business | $1,000-$5,000 | Ponemon (2024) |
| Medium Office | $10,000-$50,000 | Gartner (2024) |
| Enterprise | $100,000-$540,000 | Ponemon (2024) |
These costs underscore the importance of proactive troubleshooting and maintenance in IT network installation to avoid financial losses.
Network Installation and Upgrades
Upgrading a network is essential to maintain performance, security, and scalability for home networking installation, office network installation, and commercial network installation. Recognizing when to upgrade prevents bottlenecks and ensures compatibility with modern applications. Key signs and triggers include:
- Performance Degradation: Slow speeds or frequent dropped connections, often due to outdated hardware or cabling (e.g., Cat5 struggling with 1 Gbps demands).
- Increased Demand: Growth in users or devices, such as IoT integration, exceeding current capacity. A 2024 Gartner report notes that 70% of businesses face capacity issues within five years of initial setup.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Legacy systems lacking modern encryption (e.g., WPA3) increase breach risks by 20%, per CISA 2024.
- End-of-Life Hardware: Routers or switches no longer receiving firmware updates, compromising network set up reliability.
- New Technology Needs: Adoption of 10 Gbps applications or cloud services requiring advanced infrastructure network install.
Regular audits, recommended annually, help identify these triggers, ensuring timely network installation and upgrades.
Network Installation and Upgrades Process
The network installation and upgrades process involves a structured approach to minimize disruption and maximize performance. Steps include:
- Assess Current Network: Conduct a site survey to evaluate existing hardware, cabling, and configurations, using tools like Wireshark for performance analysis.
- Plan Upgrade: Identify required components (e.g., Cat6a for wiring an office network) and create a timeline to minimize downtime.
- Procure Hardware: Select scalable routers, switches, and cabling, ensuring compatibility with existing network equipment installation.
- Install New Components: Replace or add hardware and cabling, following a connection guide for proper termination and network cable management.
- Configure Upgrades: Update firmware, assign new IP schemes, and configure VLANs during configuring network phase.
- Test and Validate: Use cable testers and network analyzers to verify performance, addressing troubleshoot network wiring issues.
- Train Staff: Educate users on new features, especially for enterprise network setup, to ensure smooth adoption.
A 2024 TIA report notes that structured upgrades reduce implementation errors by 25%, enhancing reliability. This process applies to netzwerk installation and netværk installation, ensuring compliance with regional standards.
Upgrading from Legacy Systems (e.g., Cat5 to Cat6)
Upgrading from legacy systems like Cat5 to Cat6 addresses performance and scalability limitations. Cat5 supports only 100 Mbps over 100 meters, while Cat6 supports 10 Gbps up to 55 meters, making it ideal for modern networking installations. Key steps include:
- Replace Cabling: Swap Cat5 with Cat6 or Cat6a, adhering to T568-B standards for computer network wiring.
- Upgrade Hardware: Replace 100 Mbps routers and switches with gigabit-capable devices, critical for commercial network installation.
- Reconfigure Network: Update IP assignments and QoS settings to leverage higher speeds.
- Test Integrity: Use Fluke testers to verify new cabling, reducing connectivity issues by 20%.
A 2023 IEEE study indicates that upgrading to Cat6 improves network efficiency by 30%, supporting applications like 4K streaming and VoIP. Costs for upgrading a small office (10-20 drops) range from $500-$5,000, including $200-$1,000 for Cat6 cabling.
Future-Proofing: Preparing for 10Gbps and Beyond
Future-proofing ensures networks support emerging technologies like 10 Gbps and beyond, critical for enterprise network setup and commercial network installation. Strategies include:
- Use Cat6a or Cat7: Supports 10 Gbps up to 100 meters and 40 Gbps for shorter runs, ideal for infrastructure network install.
- Deploy Fiber Optics: Offers 100+ Gbps for long-term scalability, especially in data centers.
- Adopt Modular Hardware: Use routers and switches with upgradeable modules to handle future protocols like Wi-Fi 7.
- Implement SDN: Software-defined networking allows dynamic reconfiguration, reducing upgrade costs by 20%, per a 2024 IDC report.
- Plan for IoT: Allocate bandwidth for IoT devices, expected to reach 19.8 billion by 2025, per IoT Analytics.
Future-proofing reduces the need for frequent network installation and upgrades, saving 15-25% in long-term costs, per Gartner 2024.
Case Studies: Successful Upgrades with ROI Stats
Successful network upgrades demonstrate significant ROI through efficiency gains and reduced downtime:
- Small Business (20 Employees): Upgraded from Cat5 to Cat6 and gigabit switches. Cost: $4,000. Result: 25% faster data transfer, saving $2,000 annually in productivity.
- Retail Chain (10 Locations): Replaced legacy routers with Wi-Fi 6 and Cat6a cabling. Cost: $50,000. Result: 20% efficiency gain, yielding $15,000 annual savings and 10% sales increase.
- Enterprise Campus: Transitioned to fiber optics and SDN. Cost: $200,000. Result: 30% reduction in operational costs, saving $60,000 annually and avoiding $100,000 in downtime.
These case studies, sourced from 2024 industry reports, highlight 20-30% efficiency gains, underscoring the value of strategic upgrades.
Upgrade Cost Breakdown
| Network Type | Hardware Cost | Cabling Cost | Labor Cost | Downtime Cost | Total (Approx.) |
| Small Home (1-10 devices) | $100-$500 | $50-$500 | $0-$500 | $0-$100 | $150-$1,500 |
| Medium Office (10-50 devices) | $1,000-$5,000 | $500-$2,000 | $500-$3,000 | $1,000-$5,000 | $3,000-$15,000 |
| Large Commercial (50+ devices) | $10,000-$50,000 | $2,000-$10,000 | $5,000-$20,000 | $10,000-$50,000 | $27,000-$130,000 |
This table, based on 2024 Cabling Installation & Maintenance data, outlines upgrade costs, including minimal downtime with proper planning. Downtime costs, estimated at $1,000-$50,000 per hour, are mitigated by scheduling upgrades during off-hours.
Home Networking Wired: Diagrams and Guides
Wired home network installation provides reliable, high-speed connectivity for streaming, gaming, and smart home devices, critical for modern households in the USA. A wired home network diagram simplifies planning and execution, ensuring efficient network set up. Key steps include:
- Create a Diagram: Map cable routes from a central router to key areas (e.g., living room, office, bedrooms) using a star topology. Tools like Lucidchart or Visio are commonly used for home networking wired diagrams.
- Select Cabling: Use Cat6 cables for 1-10 Gbps speeds, supporting applications like 4K streaming. A connection guide ensures T568-B configuration for terminations.
- Install Drops: Place keystone jacks for clean connections, typically 1-5 drops for a small home.
- Test Connections: Use a Fluke tester to verify network drop installation, reducing connectivity issues by 20%.
A 2024 FCC report notes that wired home networks improve streaming reliability by 30% compared to wireless setups, making them ideal for urban homes. Costs range from $100-$1,000, depending on the number of drops and network cable management complexity.
Professional Home Network Installation Services
Professional home network installation services in the USA offer expertise for seamless setups, particularly for complex wired home network installation. Services include:
- Site Assessment: Evaluate home layout to optimize router and drop placement.
- Cabling and Hardware Setup: Install Cat6 cables, gigabit switches, and Wi-Fi 6 routers, ensuring scalability.
- Configuration: Set up QoS for streaming and WPA3 encryption for security, critical as home network attacks rose 15% in 2024, per FCC data.
- Maintenance Plans: Offer ongoing troubleshoot network wiring and firmware updates.
Professional services cost $200-$500 in labor, per 2024 HomeAdvisor data, but save 10-15 hours of DIY effort. Companies like Geek Squad or local IT firms are popular in the USA for home network installers.
Office Network Installation in Multi-Floor Buildings
Office network installation in multi-floor buildings requires careful planning to ensure reliable connectivity across floors, common in urban US business districts. Key considerations include:
- Cabling Infrastructure: Use Cat6 or Cat6a for network drop installation, with vertical risers (fiber optics for high-rise buildings) connecting floors.
- Switches and APs: Deploy managed switches (e.g., Cisco SG350) and Wi-Fi 6 access points per floor, supporting 10-50 devices per 1,000 sq ft.
- Network Server Setup: Centralize servers in a secure data closet, using VLANs to segment departments for security.
- Elevator Shaft Considerations: Route cables through conduits, adhering to NFPA 70 fire codes.
A 2024 Cabling Installation & Maintenance report estimates costs at $5,000-$20,000 for a three-floor office, with 25% of issues tied to improper riser cabling. Network cable management is critical to avoid clutter in multi-floor setups.
Commercial Network for Retail and Healthcare
Commercial network installation for retail and healthcare in the USA demands high reliability and security due to customer and patient data sensitivity. Requirements include:
- Retail: Deploy hybrid networks with Cat6 wiring for POS systems and Wi-Fi 6 for customer access. QoS prioritizes transaction traffic, boosting sales by 10%, per a 2024 retail study.
- Healthcare: Use fiber optics for fast, secure patient data transfer, with VLANs isolating medical devices. HIPAA compliance is mandatory, requiring encryption and access controls.
- Redundancy: Implement backup routers to avoid downtime, costing $5,000-$50,000/hour in retail/healthcare settings.
A 2024 healthcare IT report notes that fiber-based networks reduce data retrieval times by 25%, improving patient care efficiency. Costs range from $10,000-$50,000, depending on scale.
Global Statistics on Network Adoption
Network adoption trends highlight the growing reliance on wired and hybrid networks, particularly in the USA:
- Urban Homes: 80% of US urban homes have wired networks, driven by demand for high-speed streaming and gaming, per a 2024 FCC report.
- Business Adoption: 70% of US businesses use hybrid wired/wireless networks, with wireless traffic growing 20% annually, per Statista 2024.
- IoT Growth: 50% of US network traffic comes from IoT devices, necessitating robust network drop installation, per a 2024 IoT Analytics report.
| Metric | Value | Source |
| Urban Homes with Wired Networks | 80% | FCC (2024) |
| Businesses with Hybrid Networks | 70% | Statista (2024) |
| IoT Traffic Share | 50% | IoT Analytics (2024) |
These statistics emphasize the importance of specialized networking installations tailored to US market demands.
Essential Tools for Network Install
Effective network installation, whether for home networking installation, office network installation, or commercial network installation, relies on specialized tools to ensure precision and reliability. Essential tools for network install include:
- Cable Tester (e.g., Fluke DSX-8000): Verifies cable integrity for Cat6 B config, reducing troubleshoot network wiring issues by 20%. Cost: $500-$2,000.
- Crimping Tool: Secures RJ45 connectors for network drop installation, essential for computer network wiring. Cost: $20-$100.
- Punch-Down Tool: Connects cables to keystone jacks or patch panels in wiring an office network. Cost: $10-$50.
- Cable Stripper: Prepares cables for termination, ensuring clean cuts for install network cabling. Cost: $15-$40.
- Fish Tape: Guides cables through walls or conduits, critical for infrastructure network install. Cost: $20-$100.
- Label Maker: Enhances network cable management by labeling cables for easy identification. Cost: $30-$150.
A 2024 CompTIA study notes that using professional tools reduces installation time by 15%, saving $100-$1,000 per project for office network installation. These tools are vital for both home network installers and enterprise network setup.
Software for Monitoring and Management
Network monitoring and management software ensures optimal performance and quick resolution of issues in network set up. Key software includes:
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor: Tracks device health and traffic, reducing downtime by 15% in commercial network installation. Cost: $1,500-$5,000/year.
- Wireshark: Analyzes network traffic for troubleshoot network wiring, ideal for IT network installation. Cost: Free (open-source).
- Cisco DNA Center: Automates configuration and monitoring, cutting setup time by 40% in enterprise network setup. Cost: $10,000-$50,000/year.
- NetDisco: Manages small-scale networks, suitable for wired home network installation. Cost: Free (open-source).
- ManageEngine OpManager: Provides real-time alerts and cable mapping, enhancing network cable management software integration. Cost: $700-$2,000/year.
A 2024 Gartner report highlights that monitoring software saves $1,000-$10,000 per incident by reducing resolution time by 30%. These tools are critical for a network of computers inside an organization.
Best Practices for Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Sustainability and energy efficiency are increasingly important in networking installations, particularly in the USA, where energy costs impact operational budgets. Best practices include:
- Use Energy-Efficient Hardware: Select routers and switches with low power consumption, reducing energy costs by 10%, per a 2024 EPA report.
- Optimize Cooling: Ensure proper ventilation for network equipment installation to prevent overheating, extending hardware lifespan by 20%.
- Implement PoE: Power over Ethernet reduces cabling needs, cutting energy use by 15% in wiring an office network.
- Schedule Off-Peak Usage: Configure devices to enter low-power modes during non-business hours, saving 5-10% on energy bills.
- Recycle Old Equipment: Properly dispose of legacy hardware (e.g., Cat5 cables) to comply with US e-waste regulations.
These practices align with netzwerk installation and netværk installation standards, reducing environmental impact and operational costs.
Top Software Recommendations
| Software | Features | Approximate Cost (Annual) | Best Use Case |
| SolarWinds NPM | Real-time monitoring, cable mapping, alerts | $1,500-$5,000 | Commercial network installation |
| Wireshark | Packet analysis, troubleshoot network wiring | Free | IT network installation |
| Cisco DNA Center | Automation, configuration management, analytics | $10,000-$50,000 | Enterprise network setup |
| NetDisco | Network discovery, basic cable management | Free | Wired home network installation |
| ManageEngine OpManager | Performance tracking, compliance auditing | $700-$2,000 | Office network installation |
This table, based on 2024 industry data from Cabling Installation & Maintenance, guides software selection for various network install types. Costs reflect licensing for small to medium setups, with enterprise solutions scaling higher.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The networking industry in the USA is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements like 5G and emerging 6G technologies. Key trends and statistics include:
- 5G Integration: 60% of US businesses integrate 5G for low-latency applications, boosting network performance by 25%, per a 2024 Statista report.
- 6G Development: Early 6G trials, expected by 2030, promise 100 Gbps speeds, necessitating fiber optic infrastructure network install, per a 2024 IEEE forecast.
- IoT Expansion: 50% of US network traffic comes from IoT devices, requiring robust network drop installation, per IoT Analytics 2024.
- SDN Adoption: 25% of enterprises use software-defined networking, reducing costs by 20%, per IDC 2024.
| Trend | Statistic | Source |
| 5G Integration | 60% of businesses | Statista (2024) |
| 6G Speed Potential | 100 Gbps by 2030 | IEEE (2024) |
| IoT Traffic Share | 50% of network traffic | IoT Analytics (2024) |
These trends highlight the need for future-proof network set up, particularly for commercial and enterprise environments in the USA.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Small Home Network Setup
Scenario: A suburban US family of four needed a reliable wired home network installation to support streaming, gaming, and remote work.
Solution: A home network installer deployed a Wi-Fi 6 router, an 8-port gigabit switch, and four Cat6 network drops to the living room, home office, and two bedrooms. A wired home network diagram guided the installation, with cables routed through walls for clean aesthetics. The setup included QoS configuration for streaming prioritization and WPA3 encryption for security.
Outcome: The network supported 1 Gbps speeds, improving streaming reliability by 30%, per FCC 2024 data.
Cost: $800 ($300 hardware, $300 cabling, $200 labor).
Time: 1 day.
This setup demonstrates the effectiveness of professional home network installation for small-scale needs.
Medium Office Network Overhaul
Scenario: A 30-employee marketing firm in Chicago required an office network installation upgrade from Cat5 to Cat6 to support 50 devices, including VoIP phones and cloud-based applications.
Solution: The project involved replacing 2,000 feet of Cat5 with Cat6, installing a 24-port managed switch, and configuring VLANs for department segmentation. Network cable management software (SolarWinds) was integrated for monitoring. A Fluke tester verified network drop installation integrity.
Outcome: Data transfer speeds increased by 25%, and downtime was reduced by 15%, saving $5,000 annually, per a 2024 CompTIA report.
Cost: $10,000 ($4,000 hardware, $2,000 cabling, $4,000 labor).
Time: 3 days.
This overhaul highlights the benefits of upgrading computer network wiring for medium-sized businesses.
Large Commercial Network Deployment
Scenario: A retail chain with 50 US stores needed a commercial network installation to support POS systems, inventory management, and customer Wi-Fi.
Solution: The deployment used a hybrid network with Cat6a wiring for POS systems and Wi-Fi 6 access points for customer access. Fiber optic risers connected multiple floors in flagship stores, and redundant routers ensured 99.99% uptime. QoS prioritized transaction traffic, and VLANs isolated sensitive data.
Outcome: Transaction processing speed increased by 20%, boosting sales by 10% ($100,000 annually), per a 2024 retail study.
Cost: $200,000 ($100,000 hardware, $50,000 cabling, $50,000 labor).
Time: 10 days per store.
This case underscores the scalability of infrastructure network install for retail.
Enterprise-Level Infrastructure Upgrade
Scenario: A Fortune 500 company in New York upgraded its enterprise network setup across a multi-site campus to support 1,000+ devices, including IoT and cloud services.
Solution: The upgrade replaced Cat6 with fiber optics for 100 Gbps backbone speeds, implemented software-defined networking (SDN), and integrated Cisco DNA Center for automation. Network server setup included redundant systems, and GDPR-compliant security measures were applied for global operations.
Outcome: Operational costs dropped by 30% ($60,000 annually), and downtime costs of $100,000 per incident were avoided, per a 2024 Cisco report.
Cost: $500,000 ($300,000 hardware, $100,000 cabling, $100,000 labor).
Time: 15 days.
This upgrade showcases the ROI of future-proofing IT network installation.
Lessons Learned with Quantifiable Outcomes
- Planning Reduces Errors: Thorough site surveys and wired home network diagrams cut installation errors by 25%, saving $1,000-$10,000 per project.
- Automation Saves Time: Tools like Cisco DNA Center reduced configuration time by 40%, saving $5,000-$20,000 in labor for commercial network installation.
- Scalability Pays Off: Upgrading to Cat6a or fiber optics reduced future upgrade costs by 20%, saving $10,000 annually for medium offices.
- Proactive Maintenance: Regular audits and troubleshoot network wiring prevented 15% of downtime incidents, saving $5,000-$50,000 annually.
These outcomes emphasize the importance of strategic planning and execution in networking installations.
Conclusion
This guide has covered the essentials of network installation, from installing network cabling to advanced enterprise setups. Key takeaways include:
- Structured Installation: Following a step-by-step process for network drop installation and configuration reduces errors by 30%.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing: Using Cat6a, fiber optics, and SDN prepares networks for 10 Gbps and beyond, saving 15-25% in long-term costs.
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance: Proactive measures like cable testing and software monitoring cut downtime by 15%, saving $1,000-$50,000 per incident.
- Specialized Needs: Tailored solutions for home, office, and commercial setups, including retail and healthcare, ensure reliability and compliance with US standards like NFPA 70.
Tips for Successful Implementation
- Plan Thoroughly: Use wired home network diagrams or office layouts to map cable routes and device placement.
- Invest in Quality: Opt for pure copper Cat6 cables and enterprise-grade hardware to avoid 20% of performance issues.
- Automate Where Possible: Use tools like SolarWinds or Cisco DNA Center to streamline configuring network tasks, saving 40% in setup time.
- Prioritize Security: Implement VLANs and WPA3 encryption to reduce breach risks by 25%.
- Schedule Maintenance: Regular audits and firmware updates prevent 15% of downtime incidents.
Contact DigicoWiring for Professional Services Network Installation
For expert assistance with home networking installation, office network installation, or commercial network installation, contact DigiCoWiring. Their team specializes in tailored solutions, from wiring an office network to enterprise network setup, ensuring compliance with US standards and optimal performance. Visit www.digicowiring.com or call (323) 350.3679 for a consultation.